Oligohydramnios: Causes, Diagnosis and Symptoms
What is Oligohydramnios?
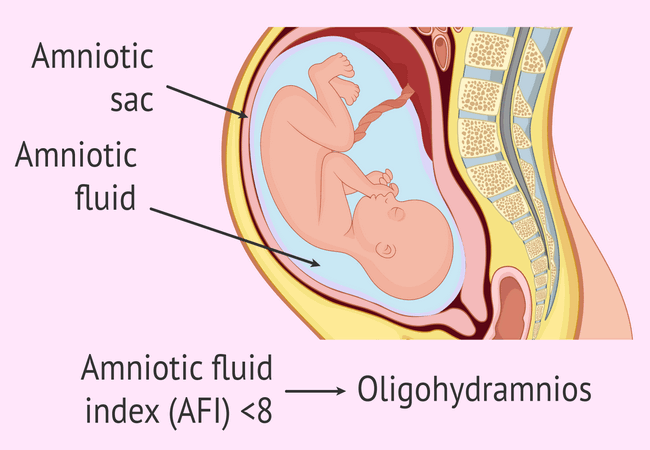
Oligohydramnios is a medical condition characterized by a lower-than-normal amount of amniotic fluid in the amniotic sac during pregnancy. Amniotic fluid is crucial for the fetus’s development as it cushions the baby, helps maintain a constant temperature, and is necessary for lung and digestive system development.

Causes of Oligohydramnios:
Causes are unknown but often associated with-
- Renal agenesis or obstruction of the fetal urinary tract.
- Placental insufficiency (IUGR).
- Fetal Abnormalities: Absence of the kidney or any other kidney abnormality (renal agenesis, polycystic kidney) in the baby can also hamper urine production.
- Genetic Factors: Inheriting abnormal genes in an autosomal recessive or autosomal dominant pattern.
- Premature rupture of membrane (PROM).
- Hypertensive disorder, dehydration.
- Drug-Induced Causes: Using NSAIDs like indometacin and certain ACE (angiotensin- converting enzyme).
PROM is the common, labor may be protected and contractions are more painful.
Signs and Symptoms of Oligohydramnios:
Clinical Features of Oligohydramnios:
The signs and symptoms of oligohydramnios vary from person to person but some of the most common signs and symptoms are:
- Rapid growth of uterus.
- Abdominal discomfort.
- Leaking of the amniotic fluid.
- Little to no or decreasing fetal movement.
- Uterine contractions.
- Abnormal findings on a fetal monitor including fetal distress.
- Abnormal protuberance of fetal parts.
- Fetal malpresentation.
- Shorter symphysis-fundus height.
Diagnosis of Oligohydramnios:
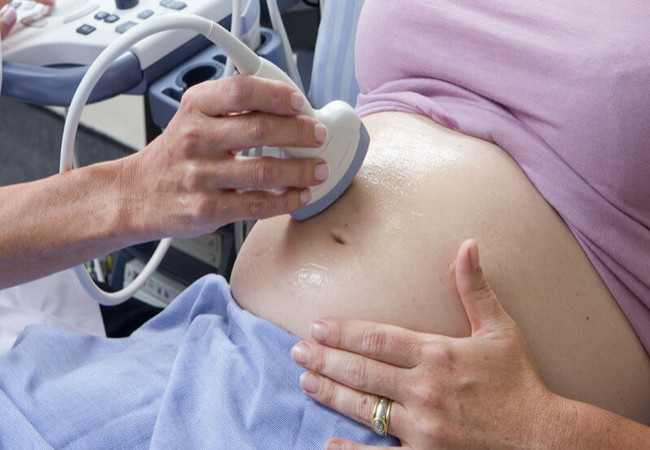
1. Ultrasound:
This helps in:
- Checking fetal growth.
- Ruling out other disorders (cystic dysplasia, ureteral obstruction, renal agenesis etc.).
- Determine placental insufficiency (by using Doppler ultrasound).
The diagnostic criteria include:
- Amniotic fluid levels lower than 5 cm.
- Absence of a 2-3 cm deep fluid pocket.
- The total amniotic fluid volume below 500mL between 32nd and 36th gestational o weeks.
2. Amniotic Fluid Index (AFI):
There are a number of tests available for measuring the amniotic fluid volume (AFV), with AFI being the most commonly used procedure. Around 8% of all pregnant women may have low amniotic fluid levels with 4% among them diagnosed with oligohydramnios.
3. Maximum Vertical Pocket (MPV):
This test allows doctors to check the amniotic fluid levels in the deepest part of the uterus.
4. Sterile Speculum Examination:
It helps to detect any rupture of membranes (ROM) responsible for oligohydramnios.
5. Maternal Blood Test:
6. Blood tests, like maternal serum screening, can be performed to detect low levels of amniotic fluid in the uterus as well as to determine the chances of the baby being born with congenital disorders like Down syndrome and spina bifida.
More questions related to this article:
- Define oligohydramnios.
- What do you mean by oligohydramnios?
- What is oliamnios?
- What are the causes of oligohydramnios?
- Mention the clinical features of oligohydramnios?
- List the signs and symptoms of oligohydramnios?
- What are the clinical features of oligohydramnios?
- What are the diagnoses of oligohydramnios?
- What are the tests and monitoring needed for oligohydramnios?