Placenta Praevia: Types, Symptoms, Diagnosis
What is Placenta Praevia?
When the placenta is implanted partially or completely over the lower uterine segment, it is called placenta praevia. Placenta previa is an obstetric complication in which the placenta is inserted partially or wholly in the lower uterine segment. It is a leading cause of antepartum haemorrhage (vaginal bleeding). It affects approximately 0.4-0.5% of all labours.

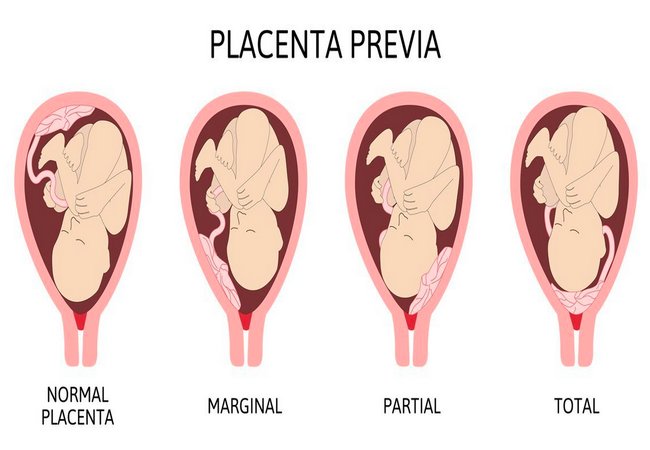
Degree or Types of Placenta Praevia:
It includes the following:
- Type I (low Iying): The major part of the placenta is attached to the upper segment and 10 21 only the lower margin encroaches onto the lower segment but not up to the OS.
Type 2 (Marginal): The placenta reaches the margin of the internal OS but does not cover it.
Type3 (Incomplete or partial central): The placenta covers the internal OS partially.
Type 4 (Central or total): The placenta completely covers the internal OS even after it is fully dilated.
For clinical purpose, the types are graded in to-
- Mild degree (Type 1 & 2 anterior),
- Major degree (Type 2, 3 &. type 4).
Sign and Symptoms of Placenta Praevia:
Clinical Features of Placenta Praevia:
1. Symptoms of placenta praevia:
Vaginal bleeding: Sudden onset, painles, apparently causeless and recurrent.
2. Signs of placenta praevia:
a) General signs: Anemia
b) Abdominal examination:
- The size of the uterus is proportionate to the period of gestation.
- The uterus feels relaxed, soft, elastic and not tender.
- The head is floating.
- Fetal heart sound is present.
- Persistence of mal-presentation.
c) Per vaginal examination: On inspection, the blood is bright red.
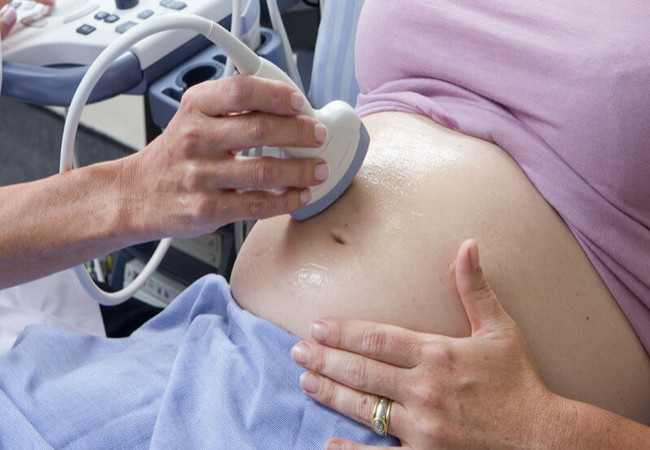
Investigation or Diagnosis of Placenta Praevia:
It includes the following:
- Blood for TC, DC, Hb% and ESR,
- Blood grouping and Rh. typing,
- Blood sugar,
- Serum creatinine,
- Urine for RME,
- Chest X-ray,
- ECG,
- Ultrasonogram.
Risk Factors of Placenta Praevia:
1. Previous Cesarean Delivery:
Scar tissue from previous surgeries can affect placenta placement.
2. Previous Placenta Praevia:
History of the condition increases the likelihood in subsequent pregnancies.
3. Multiple Pregnancies:
Women with multiple pregnancies or those carrying multiples (twins, triplets) have a higher risk.
4. Advanced Maternal Age:
Women over 35 are at increased risk.
More questions related to this article:
- What do you mean by placenta praevia?
- Define placenta praevia?
- Write down the types or degree of placenta praevia?
- Mention the types or degree of placenta praevia?
- Write down the types of placenta praevia?
- Write down the clinical features of placenta praevia.
- What are the sign and symptoms of placenta praevia?
- How will you investigate placenta praevia?
- Mention the investigation or diagnosis of placenta praevia.
- What are the risk factors of placenta praevia?