Placenta Praevia: Treatment, Management, Complications
Definition of Placenta Praevia:
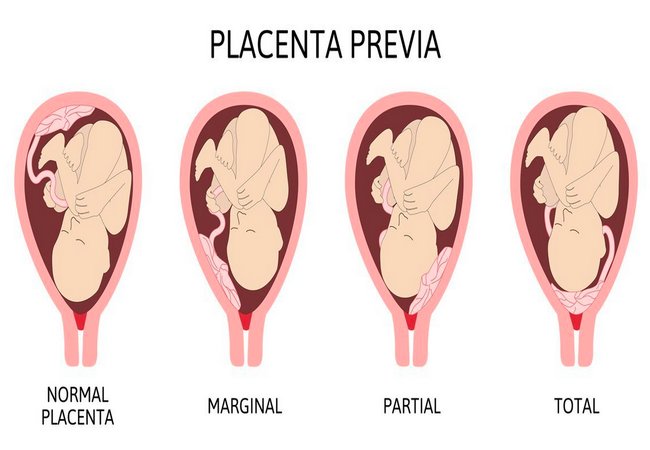
When the placenta is implanted partially or completely over the lower uterine segment, it is called placenta praevia. Placenta previa is an obstetric complication in which the placenta is inserted partially or wholly in the lower uterine segment. It is a leading cause of antepartum haemorrhage (vaginal bleeding). It affects approximately 0.4-0.5% of all labours.

Treatment and Management of Placenta Praevia:
At home:
1. Patient is immediately put to bed.
2. To assess the blood loss-
- Inspection of the clothing soaked with blood
- To note the pulse, BP, anemia.
3. Quick but gentle abdominal examination to mark the height of the uterus, to auscultation of the fetal heart sound and to note any tenderness on the uterus.
4. Vaginal examination must not be done.
Transfer to hospital and admission to hospital:
Immediate attention:
- Amount of the blood loss.
- Blood samples are taken for group, cross matching and estimation of Hb%.
- An infusion of normal saline.
- Gentle abdominal palpation.
- Inspection of the vulva to note the presence of any active bleeding.
Formulation of the line of treatment:
1. Expectant treatment:
The aim is to allow the pregnancy to continue until baby grown sufficient enough to survive ex-utero.
Prerequisites:
- Availability of blood for transfusion
- Facilities for caesarean section available throughout 24 hours.
Selection of cases-
- Pregnancy is less than 37 weeks.
- Good maternal and fetal condition.
- No active bleeding.
2. Active treatment:
- Bleeding occurs at or beyond 37 weeks of pregnancy.
- Patient is in labour.
- Patient is in exsanguinated state on admission.
- Bleeding in continuing and of moderate degree.
- Baby is dead or known to be congenital deformed.
Definitive treatment:
a) Vaginal examination:
If the diagnosis is still uncertain after ultrasound examination, a pelvic examination is performed when the pregnancy is near term. It is done in the operation theatre with the woman anaesthetized and the instruments sterilized and ready for caesarean section.
b) Termination of pregnancy:
1. ARM (low rupture of the membrane): If placenta praevia type 1 or type 2 anterior.
2. Caesarean section:
- Placenta praevia type 2 posterior, type 3, type 4.
- Other indications for caesarean section.
Complications of Placenta Praevia:
1. Maternal:
a. During pregnancy:
- Ante-partum hemorhage with varying degrees of shock.
- Mal-presentation.
- Premature labour.
b. During labour:
- Early rupture of membrane,
- Cord prolapsed,
- Slow cervical dilatation,
- Intra-partum hemorrhage,
- PPH,
- Retained placenta.
c. Puerperium:
- Puerperal sepsis,
- Subinvoluation.
2. Fetal:
- Low birth weight,
- Birth asphyxia,
- Intra-uterine death,
- Birth injury,
- Congenital malformation is three times more common.
More questions related to this article:
- What do you mean by placenta praevia?
- Define placenta praevia?
- What is placenta praevia?
- How will you treat a case of placenta praevia?
- How will you mange placenta praevia?
- Write down the management of a case of 34 wk pg. with P/V bleeding.
- Write down the complication of placenta praevia.
- What are the complications of placenta praevia?