Tubal Pregnancy: Symptoms, Causes and Treatment
What is Tubal Pregnancy?
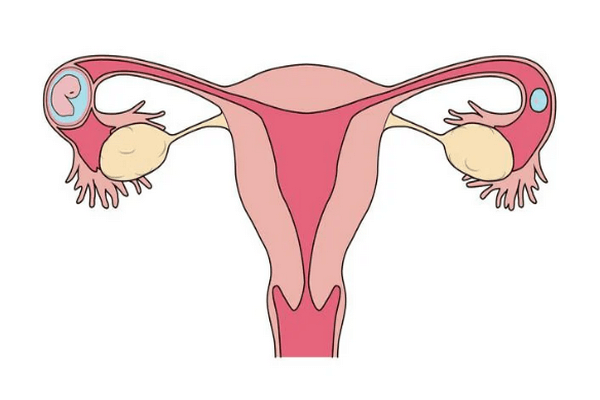
A pregnancy that is not in the usual place within the uterus but is located in the Fallopian tube is called tubal pregnancy. Tubal pregnancies are due to the inability of the fertilized egg to make its way through the Fallopian tube into the uterus. Or Implantation of the fertilized ovum in the fallopian tube is called tubal pregnancy.

Sign and Symptoms of Tubal Pregnancy:
It includes the following:
1. Abdominal Pain:
Sharp or stabbing pain in the abdomen, often localized on one side.
2. Shoulder Pain:
Caused by internal bleeding irritating the diaphragm.
3. Vaginal Bleeding:
Light to heavy bleeding that might be mistaken for a period.
4. Dizziness or Fainting:
This can result from significant internal bleeding.
Aetiology or Causes of Tubal Pregnancy:
Abnormalities of the tube delaying or preventing the progress of fertilized ovum –
- Developmental errors; Hypoplasia, undue tortuosity divèrticula and accessory lumina.
- Distortion of the tube by large tumour or endometriosis.
- Previous inflammatory disease (salpingitis). Narrowing of the tubal lumen, intratubal adhesions, peritubal adhesions.
1. Surgical –
- After partial salpingectomy,
- After tubal ligationor hysterectomy (If operation is performed within 48hrs of coitus) Tubal plastic surgery- (microsurgery and reversal sterilization).
- Inefficient tubal contractions or a poor cilial current: Developmental anomalies, results of previous infection.
- IUCD.
2. Overdevelopment of the ovum- external migration:
An ovum discharged from one Ovary can be fertilized in the peritoneal cavity and cross the pelvis by a process of external migration to enter the opposite tube. Meanwhile the fertilized ovum biggers in size and may be too big to pass isthmic portion of the tube.
3. Endometriosis of the fallopian tube.
Diagnosis of Tubal Pregnancy:
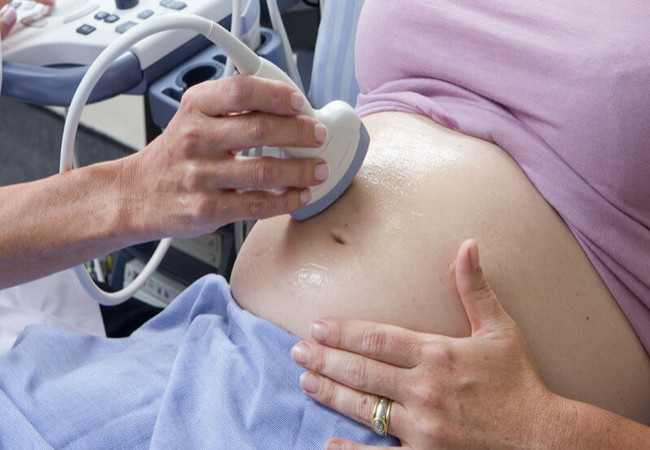
a. Ultrasound:
A transvaginal ultrasound is often used to confirm the location of the pregnancy.
b. Blood Tests:
To measure hCG levels, which can indicate abnormal pregnancy progression.
Treatment of Tubal Pregnancy:
1. Medication:
Methotrexate may be used to stop the growth of the pregnancy in early stages.
2. Surgery:
If the tube has ruptured or if the pregnancy is advanced, surgical intervention may be necessary. This can involve removing the pregnancy (and sometimes the tube) via laparoscopy.
Outcome or Termination of Tubal Pregnancy:
A tubal pregnancy may terminate in one of the following ways and usually before it is 6 weeks old. Tubal abortion (Intratubal rupture- discharge of ovum into the lumen of the tube. One of four things may happen-
- Complete absorption,
- Complete abortion,
- Incomplete abortion,
- Missed abortion- tubal mole,
- Tubal rupture,
- Intra-peritoneal rupture,
- Extra-peritoneal rupture.
More questions related to this article:
- Define tubal pregnancy.
- What is the definition of tubal pregnancy?
- What does mean tubal pregnancy?
- What are the causes of tubal pregnancy?
- Mention the Aetiology of tubal pregnancy?
- Write down the termination of tubal pregnancy.
- Discuss the outcome of tubal pregnancy.
- What are the sign and symptoms of tubal pregnancy?
- Mention the diagnosis of tubal pregnancy.
- Mention the treatment of tubal pregnancy.