Management of Multiple Pregnancy or Twin Pregnancy
What is Multiple Pregnancy?
When more than one fetus simultaneously develops in the uterus, it is called multiple pregnancy.
Management of Twin or Multiple Pregnancy:
Assessment of multiple pregnancy:
- History of ovulation inducting drugs specially gonadotrophin, for infertility or use of ART.
- Family history of twining (more often present in the maternal side).

Symptoms of multiple pregnancy:
- Minor ailment of normal pregnancy is often exaggerated. Some of the symptoms are related to the undue enlargement of the uterus.
- Increased nausea and vomiting in early months.
- Cardio-respiratory embarrassment which is evident in the later months -such as palpitation or shortness of breath.
- Tendency of swelling of the legs, varicose veins and hemorrhoids is greater.
- Unusual rate of abdominal enlargement and excessive fetal movements may be noticed by an experienced parous mother.
You can read: Classification or Types of Twin or Multiple Pregnancy
General examination:
- Prevalence of anaemia is more than in single pregnancy.
- Unusual weight gain, not explained by preeclampsia or obesity, is an important feature.
- Evidence of preeclampsia (25%) is a common association.
Abdominal examination:
Inspection:
1. The elongated shape of a normal pregnant uterus is changed to a more “barrel shape” and the abdomen is unduly enlarged.
2. The height of the uterus is more than the period of amenorrhoea.
3. Finding of two fetal heads or three fetal poles make the clinical diagnosis almost certain.
4. The girth of the abdomen at the level of umbilicus is more than the normal average atterm (100 cm).
- Fetal bulk seems disproportionately large in relation to the size of the fetal head.
- Palpation of too many fetal parts.
Auscultation:
Simultaneous hearing of two district fetal heart sounds located at separate spots with a silent area in between by two observers, gives a certain clue in the diagnosis of twins, provided the difference in heart rate is at least 10 beat per minute.
Internal examination:
- In some cases, one head is felt deep in the pelvic, white the other one i located by abdominal examination.
Investigation:
Ultrasonography to detect –
- 2 gestational sacs (at 10h weeks)
- 2 fetal heads at 14th weeks.
In multifetal pregnancy it is one to obtain the following information;
- Confirmation of diagnosis as early as 10 weeks of pregnancy.
- Viability of fetuses.
- Chorionicity (lambda or twin peak sign).
- Pregnancy dating.
- Fetal anomalies.
- Fetal growth monitoring (at every3-4 weeks interval) for IUGR.
- Presentation and lie of the fetuses.
- Twin transfusion (Doppler ‘studies).
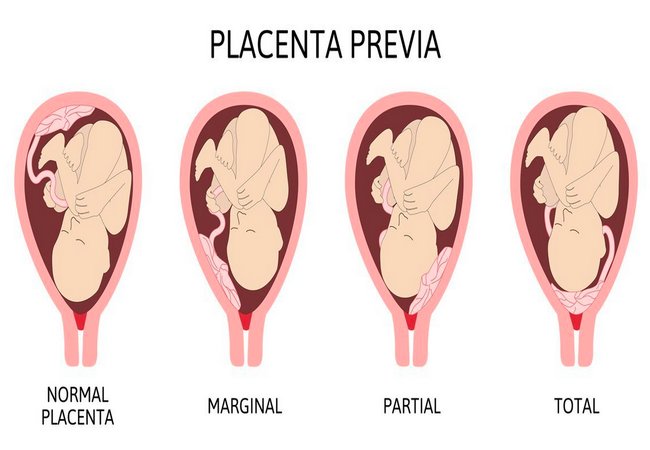
- Placental localization.
- Amniotic fluid volume.
You can read: Causes and Complications of Twin or Multiple Pregnancy
Management During Labour (Place of Delivery: Hospital):
1. First stage:
Usual conduction of the first stage as outlined for a singleton fetus is to be followed with additional precautions:
- A skilled obstetrical should be present.
- The patient should be in bed to prevent early rupture of the membranes.
- Use of analgesic drugs is to be limited as the babies are small and rapid delivery may occur.
- Careful fetal monitoring is to be done with available gadgets.
- Internal examination should be done soon after the rupture of the membranes to exclude cord prolapse.
- An intravenous line with ringer’s solution should be set up for any urgent intravenous therapy, if required.
- One unit of compatible and cross matched should be made readily available.
- Neonatologist should be present at the time of delivery.
2. Second stage:
The delivery should be conduct in the same guidelines as mentioned in normal labour:
- Liberal episiotomy under local infiltration with 1% lignocaine.
- Forceps delivery, if needed.
- Do not give intravenous ergometrine with the delivery of the anterior shoulder of the first baby.
- Clanp the cord at two places and cut in between.
- At least, 8-10 cm of cord is left behind for administration of any drug or transfusion, if required.
- The baby is handed over to the nurse after labeling it as number 1.
Delivery of the 2nd baby:
Principles:
- Delivery of the 2nd baby without must be done without undue prolongation.
3. Third Stage:
- 2 ampoule oxytocin i/v/or i/m immediately just after delivery of the baby.
- Controlled cord traction.
- Fundal massage.
- The patient is to be watched carefully for about 2 hours after delivery.